
Salt Pollution Regulations
State & Federal Regulations on Salt Pollution
Regulations surrounding the salt pollution issue are already in effect, with a focus on proper management and disposal of industrial brine wastewater. Various methods, including hauling, solar evaporation, and alternative treatments, are being employed to comply with these regulations, but existing practices often entail high costs for businesses.
There is a growing recognition of the need to update regulations to ensure the quality of reclaimed water. Water softeners are being identified as a top source of salt pollution, prompting regulatory measures and incentive programs in several states. Despite challenges, initiatives at both the state and federal levels are aiming to reduce salt pollution.

Thoughts About Salt Management
- Industrial brine generators are mandated to manage and dispose of wastewater, using methods like hauling, solar evaporation, and alternative treatments.
- Some regulations focus on specific pollutants, but there is a call for more comprehensive measures addressing multiple pollutants, particularly salt.
- Current management practices incur substantial costs for businesses and often miss opportunities for water re-use through salt reduction.
- Water softeners are increasingly recognized as sources of salt pollution, leading to regulatory measures in various communities.
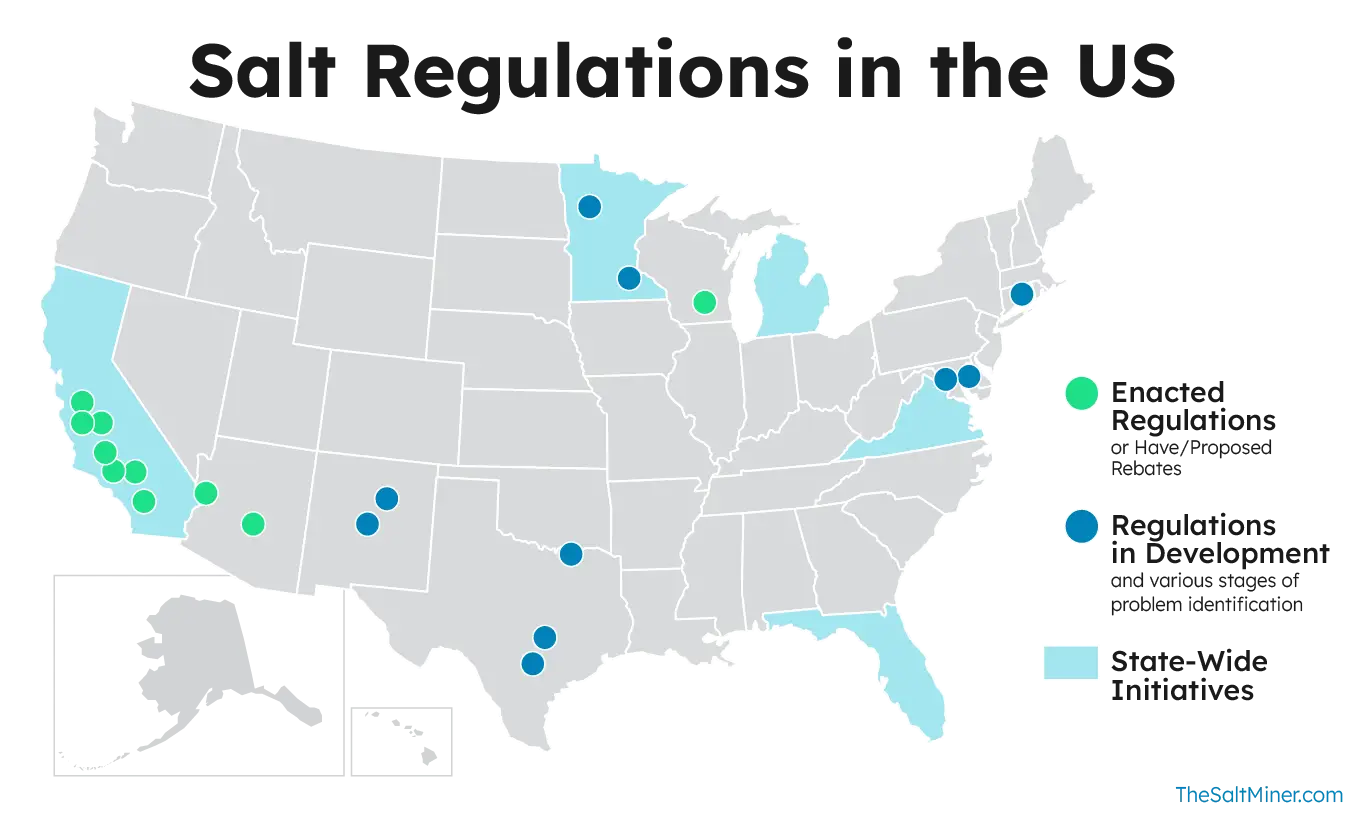
- Several states, such as California, Arizona, Wisconsin, Michigan, Delaware, Florida, and Connecticut, have enacted or considered regulations and incentives to curb softener-related salt discharge.
- Utilities are exploring alternative strategies as banning water softeners faces political challenges.
- California mandates water management entities to have salt and nutrient management plans.
- The Bureau of Reclamation leads a major initiative, in collaboration with federal agencies, to reduce salts, offering funding through multiple programs.
Examples of Current
Salt Regulations
California Regulations
- Over 50 communities in California have enacted regulations addressing salt pollution.
- State mandates water management entities to have salt and nutrient management plans.
Arizona Initiatives
- Scottsdale, Arizona offers rebates to homeowners who remove water softeners, recognizing them as a potential source of salt pollution.

Wisconsin Programs
- Madison, Wisconsin provides rebates to businesses that reduce water softener salt discharge.
- The city is exploring incentives for homeowners, as 92% of homes have water softeners.
Michigan Bans
- Michigan has implemented more bans than any other state, concerned about potential failures of septic systems due to softener discharge.
Minnesota Chloride Management
- Twenty-four communities in Minnesota, grappling with high chloride levels in wastewater, are urging homeowners to minimize the use of water softeners.

Regulations in Delaware, Florida, and Connecticut
- Delaware, Florida, and Connecticut specifically regulate softener discharge to septic systems.
Federal Initiative - Bureau of Reclamation
- The Bureau of Reclamation spearheads a major initiative, collaborating with federal agencies like the Environmental Protection Agency, the US Department of Agriculture, and the US Geological Society, to reduce salts. Funding is available through multiple programs within these agencies.
